After publication on February 18 of results showing that almost two thirds of students had failed in the Form IV (O’level) secondary school examinations, President Kikwete felt the need to assure the public on radio that education remained at the top of his administration’s list of priorities. He said that his government was touched by the massive number of failures. “It is a shock that, even schools with a well-known history of good performance such as seminaries, privately owned as well as old government schools, performed so dismally…we have to find out why,” He said that various analysts had pointed to reasons for the failure, but that his government would not rely on hearsay. He had therefore asked the Prime Minister to set up a Commission of Enquiry. He noted that the Commission would help the government and other stakeholders to take decisive measures early so as to avert further problems in the future.
Mr Kikwete allayed fears that there was a lack of political will to improve the quality of education in the country, saying: “That is why we allocated about TShs 3.6 trillion in our budget specifically towards the education sector.”
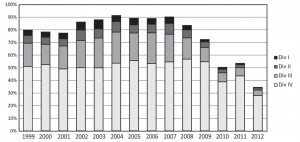
Form IV results from 1999 to 2012 (source wavuti.com & necta.go.tz) (These figures exclude pupils who registered but did not attend examinations)
‘Worst in Tanzania’s history’
The results were the worst in Tanzania’s history with only 35% of the 367,750 candidates who sat the Form IV exams in October 2012 achieving a pass – a substantial drop from the previous year’s 54% pass rate, itself well down on previous years.
There have been similar downward trends in Standard VII results and the Primary School Leaving Exam, where the pass rate dropped from 57% in 2011 to 30% in 2012. Uwezo surveys of literacy and numeracy since 2010 have painted a bleak picture.
But it was these Form IV results which saw the greatest outcry, and within days there was a buzz of activity with numerous committees investigating what needs to be done.
Summary of results
The National Examination Council of Tanzania (NECTA) records four levels of student performance – Divisions I, II, III and IV. Detailed results were as follows:
Division I: 1,641 students (0.4%)
Division II: 6,453 students (1.8%)
Division III: 15,426 students (4.2%)
Division IV: 103,327 students (28.1%)
Failed: 240,903 students (65.5%)
(these figures exclude students who registered but did not attend the examination)
Education Minister under fire
Mwesiga Baregu, a civics professor at Saint Augustine University of Tanzania, was quoted in the Somali newspaper Sabahi as saying that Minister of Education Shukuru Kawambwa should resign. “If the minister is a leader with integrity and responsibility regarding education in this country, he should resign without waiting for pressure from outside. If the minister refuses, President Kikwete should fire him.” Freeman Mbowe, Chairman of the Leading opposition party CHADEMA, said he had organised several public rallies since the examination results were announced to pressure Kawambwa to step down.
Retired secondary school teacher Yusuf Halimoja, 79, was quoted in the media as saying that the education system had declined because well-educated people no longer wanted to be teachers. “I started teaching in 1953. At that time, you could not become a teacher without a first or second class [ranking]. Because of this, teachers were respected and knowledgeable…But nowadays, the first, second and third class [rankings] pursue other professions and those with fourth class are sent to teach. That is wrong.”
The Commission
Prime Minister Mizengo Pinda’s 15-man Commission of Enquiry is led by the Executive Secretary of the Tanzania Commission for Universities (TCU), Professor Sifuni Mchome. Its remit is to understand why the Form IV results were so poor and to make recommendations to prevent this happening again.
The NCCR-Mageuzi MP, James Mbatia, refused to join the group feeling it “might create a conflict of interest as he is still pursuing the private motion on the education sector he submitted in parliament” in February. He highlighted the errors in various Government-approved English textbooks as evidence of “deficiencies in the country’s education system and the alleged corruption encroaching it”. Other areas which needed addressing were the policy framework, curriculum (there were questions over its legality) and the “dire lack of teachers”.
The Prime Minister said the Commission would work for six weeks starting on March 4 to review past performance, consider a rescheduled examination for failing students and to determine whether the transfer of educational operations from the federal to local governments contributed to the poor results.
At Tanzanian Education Network (TEN/MET)’s Quality Education Conference in early March to discuss the “standard of education in the country”, the Children’s Book Project reiterated Mbatia’s concern about the quality and management of textbooks and called for authors to be trained in writing appropriate texts for teachers and pupils. Cathleen Sekwao of TEN/MET expressed concern about the overloaded primary school syllabus. “It puts too much of a burden on the pupils to learn so much in such a short time defeating the very purpose of the books as the pupils learn less under such pressure.” As an example, Sekwao said that “Standard One pupils formerly were studying only three subjects, reading, writing, arithmetic compared to eight subjects taught today.”
The concern about education has led to the release of some significant statistics which give the background to the exam crisis.
– 1,640,969 the target for Standard 1 enrolment in 2004
– 1,368,315 the number of children who were actually enrolled
– 272,654 the enrolment shortfall, which was attributed to “massive enrolments in the first year of PEDP of 11 to 13-year-olds in grade I”
– 3 number of known suicides linked to the Form IV results
– 15,283 new teachers targeted by local authorities (no year given)
– 10,788 Grade IIIA teacher trainees enrolled in teachers’ colleges
– 10,037 number of these in government teachers’ colleges
– 751 number of these in private teachers’ colleges.
– 4:1 Pupil:book ratio in standard I-IV
– 6:1 Pupil:book ratio in standards V to VII
– 8,000 number of pregnant girls who drop out of school each year, leading to a call for sex education to be introduced into schools
Efforts to improve education
Tanzania is already making considerable efforts or planning to do so in different parts of the country to improve education:
In Mid-February, the Parliamentary Committee responsible for education invited Village Education Project Kilimanjaro to share its findings and recommendations on improving English in Tanzania.
The New Original English Course (NOEC), recently updated with all explanations and instructions in the teachers’ books now in Kiswahili, was featured on various breakfast talk-shows and in the press. The course covering Standards III to VII ensured that pupils were sufficiently fluent in English to continue their later studies in English and is seen as an immediate practical solution to rescue the education system from the ‘intensive care unit’.
115 students across 48 schools in Temeke District have benefited from funding by the Parastatal Pension Funds (PPF) through the ‘Education Benefit’ programme which is granted to children of any PPF member who passes away during their service period”.
On 11 October 2012, Salma Maoulidi contributed a piece to the Daily News on how education today compared with that of the 1977 constitution which set out to remove the class divide amongst Tanzanians. She concluded: “There is no Minister, Principal Secretary, MP, RC or DC who sends his or her child to a ward school. If national leaders, who make and implement policy, don’t want to subscribe indeed to policies they pass or swear to uphold why should the common person be expected to stomach the same?’
In launching the new Annual Teachers Awards ceremony, Chairman of the Education and Expedition Agency Association, Emmanuel Mjema ‘challenged the government to provide direct financial incentives to teachers in public and private schools countrywide so as to help improve the education standard.’ The first ceremony was on 25 November (Guardian 23/11).
Mauritius is to introduce student exchange programmes with Tanzania and other African countries as a way to enable them to obtain international experience.
St John’s University has managed to curb cheating by assuming that any cheating starts with leaked papers by the person who sets the paper. The Vice Chancellor noted that there should be no negotiation as cheating was a serious crime which was harmful to academic pursuit and detrimental to the country.

